
The date of payment is the date that payment is issued to the investor for the amount of the dividend declared. However, the purchase of treasury stock does not affect the legal capital (i.e. paid-in capital) of the company. This is due to the number of issued shares does not change due to the purchase of treasury stock. The company unfavorable variance definition needs to spend cash to purchase these kinds of investments. After purchasing the share, company has to record the marketable security which is the current assets on the balance sheet. You have just obtained your MBA and obtained your dream job with a large corporation as a manager trainee in the corporate accounting department.
Small Business
This journal entry will increase both total assets on the balance sheet and total revenues on the income statement as a result of the dividend received from the investment that we have in another company. Stock investments account is an asset account on the balance sheet, in which its normal balance is on the debit side. Likewise, in this journal entry, there is no impact on the total assets of the balance sheet as it results in the increase of one asset (stock investment) and the decrease of another asset (cash). The total stockholders’ equity on the company’s balance sheet before and after the split remain the same. This section explains the three types of dividends—cash dividends, property dividends, and stock dividends—along with stock splits, showing the journal entries involved and the reason why companies declare and pay dividends.
Popular Contents $type=blogging$count=6$author=hide$comment=hide$label=hide$date=hide$hide=home$s=0
For example, on June 9, the company ABC purchases 10,000 shares of common stock of the company XYZ. The company ABC pays $10 per share and the 10,000 shares that it owns represent 10% of the ownership in XYZ. Figure 14.5 shows what the equity section of the balance sheetwill reflect after the preferred stock is issued. When you purchase 50 shares at $40 per share, the accounting system does not care about the number of shares or the price.
Please Sign in to set this content as a favorite.
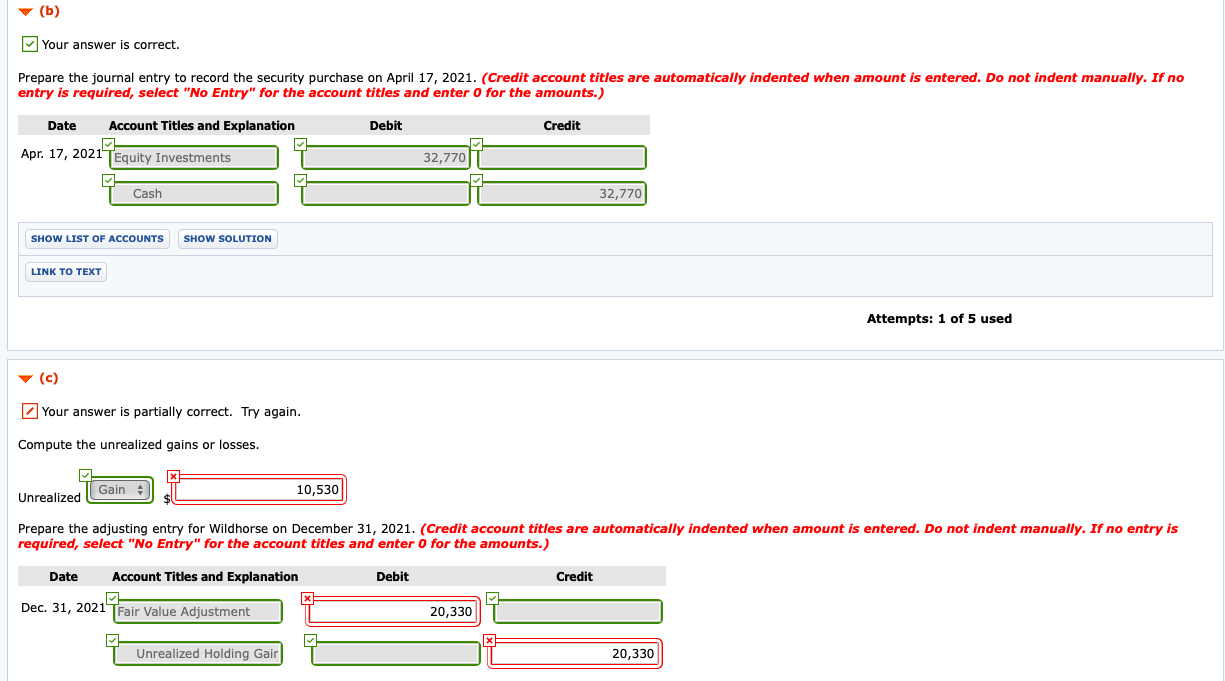
Stock with no par value that has been assigned a stated value is treated very similarly to stock with a par value. Investments in trading securities are always shown on the owner’s balance sheet at fair value. Gains and losses reported in the income statement parallel the movement in value that took place each period. The gain here is labeled as “unrealized” to indicate that the value of the asset has appreciated but no final sale has yet taken place. The gain is not guaranteed; the value might go back down before the shares are sold. However, the unrealized gain is recognized and reported on the owner’s Year One income statement.
And such dividends may need to be recorded as the dividend revenue or as the reduction of the stock investment. We can make the journal entry for investment in shares of another company by debiting the stock investment and crediting the cash account. Additionally, when we receive the dividend from the investment that we have made by purchasing shares of another company, we also need to record it into our accounting record. Though, we may record the cash dividend received as the dividend revenue or as a reduction of our investment balance depending on the percentage of ownership we have in the investee company.
It’s vital that all your transactions are entered properly so that your books can be well balanced. QuickBooks Desktop is a great software able to help you keep track of assets, liability, and equity of your business to see the financials of your company. I can point you in the right direction for assistance with this entry. Record the stock purchase as a debit to Business Stock (asset account) and credit to either cash or equity depending on where the closing funds came from. The declaration to record the property dividend is a decrease (debit) to Retained Earnings for the value of the dividend and an increase (credit) to Property Dividends Payable for the $210,000. ACCA’s technical factsheet, Company purchase of own shares, includes accounting treatment along with journal entries for all the methods discussed above.
Each share of the company’s common stock is sellingfor $25 on the open market on May 1, the date that Duratechpurchases the stock. Duratech will pay the market price of thestock at $25 per share times the 800 shares it purchased, for atotal cost of $20,000. The following journal entry is recorded forthe purchase of the treasury stock under the cost method. Assume Duratech’s net income for the first year was $3,100,000, and that the company has 12,500 shares of common stock issued. During May, the company’s board of directors authorizes the repurchase of 800 shares of the company’s own common stock as treasury stock. Each share of the company’s common stock is selling for $25 on the open market on May 1, the date that Duratech purchases the stock.
- No change to the company’s assets occurred; however, the potential subsequent increase in market value of the company’s stock will increase the investor’s perception of the value of the company.
- Companies often make the decision to split stock when the stock price has increased enough to be out of line with competitors, and the business wants to continue to offer shares at an attractive price for small investors.
- Moreover, on the maturity date, the issuer has to pay back the principal amount.
On the other hand, company can issue equity security such as common stock or preferred stock. It means they sell part of the company to the investors, and they will become the owners of the company. The investors will be able to receive the dividend base on the profit and board approval. To illustrate, assume that Duratech Corporation’s balance sheet at the end of its second year of operations shows the following in the stockholders’ equity section prior to the declaration of a large stock dividend. U.S. GAAP requires investments in trading securities to be reported on the balance sheet at fair value.
Sometimes, we may make the investment in shares of another company in order to earn extra revenues from the dividend or from the capital gain when the share price increases. In this case, we need to make the journal entry for investment in shares of another company by recognizing it as an asset on our balance sheet. In this journal entry, while the stock investments account increases by $100,000, the cash account decreases by the same amount.
Just after the issuance of both investments, the stockholders’ equity account, Common Stock, reflects the total par value of the issued stock; in this case, $3,000 + $12,000, or a total of $15,000. The amounts received in excess of the par value are accumulated in the Additional Paid-in Capital from Common Stock account in the amount of $5,000 + $160,000, or $165,000. A portion of the equity section of the balance sheet just after the two stock issuances by La Cantina will reflect the Common Stock account stock issuances as shown in Figure 14.4. The cost method is commonly used for this transaction due to its simplicity.
Cash and property dividends become liabilities on the declaration date because they represent a formal obligation to distribute economic resources (assets) to stockholders. On the other hand, stock dividends distribute additional shares of stock, and because stock is part of equity and not an asset, stock dividends do not become liabilities when declared. The company plans to issue most of the shares in exchange forcash, and other shares in exchange for kitchen equipment providedto the corporation by one of the new investors.

Recent Comments